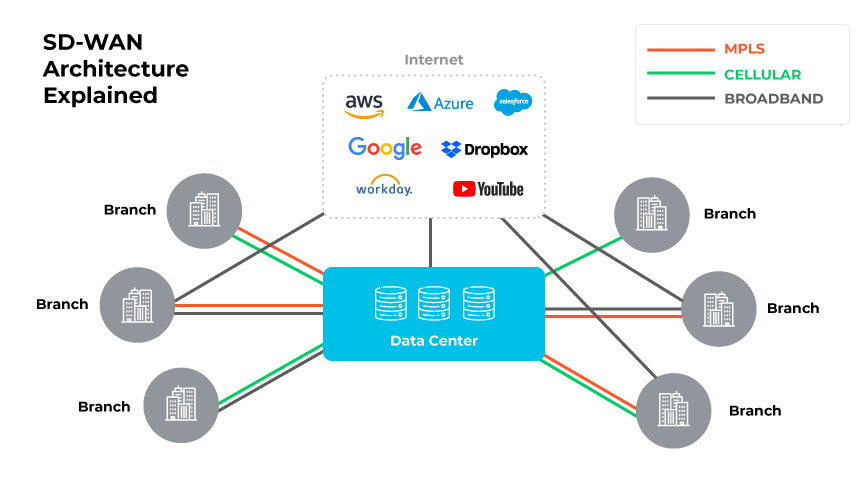
What Is Hybrid SD-WAN?
Hybrid SD-WAN is a combination of SD-WAN services and MPLS that explicitly integrates traditional MPLS with other connections like broadband and LTE. It works well for organizations that still rely on MPLS for certain critical applications but want to enhance their network with the additional flexibility and cost savings of SD-WAN.
From traditional WANs to hybrid SD-WAN: an evolution in networking
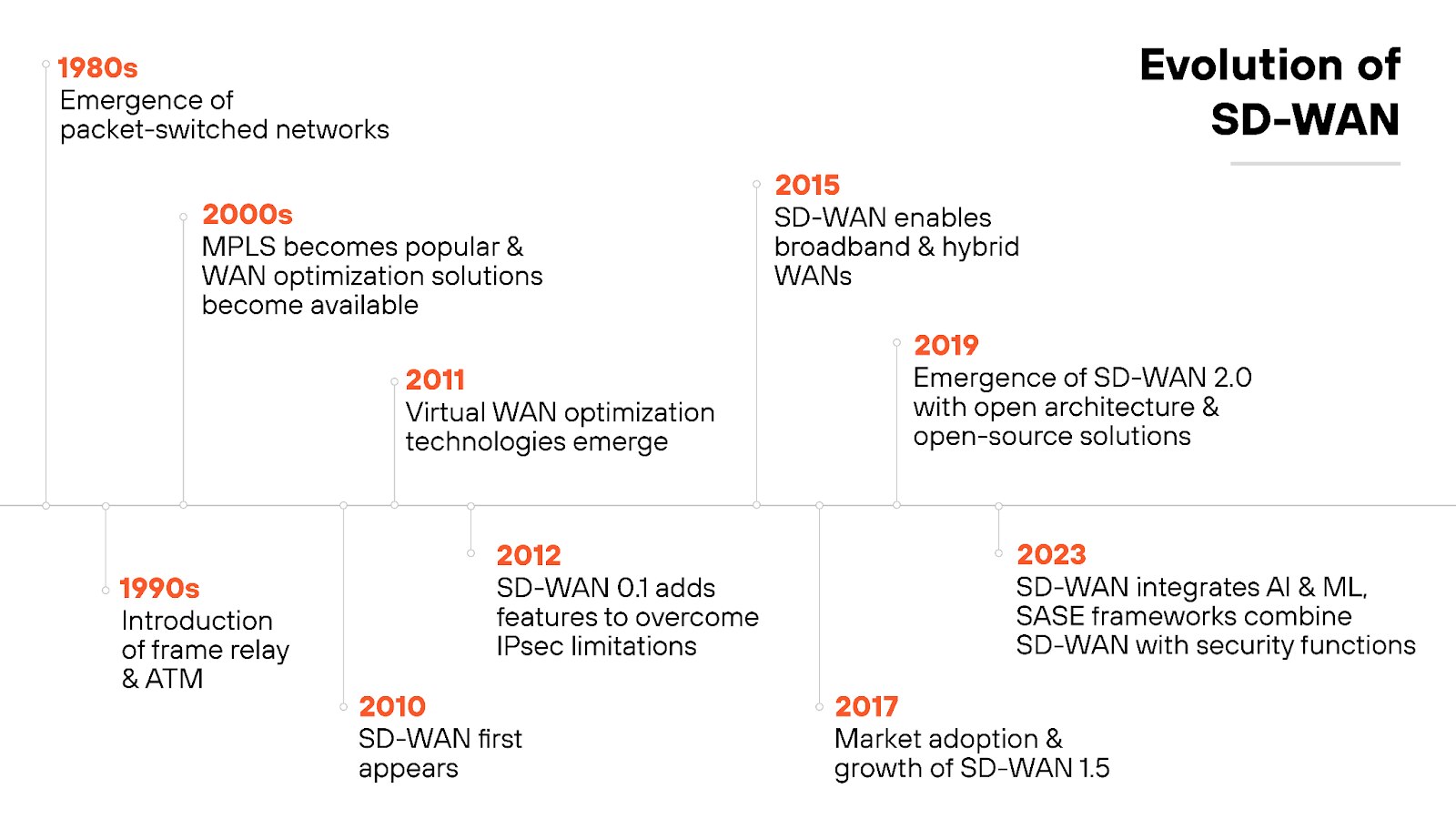
Traditional WANs were built to connect various branches of an organization to the central network, relying heavily on MPLS (multi-protocol label switching) for reliable, predictable performance.
However, MPLS had its limitations.
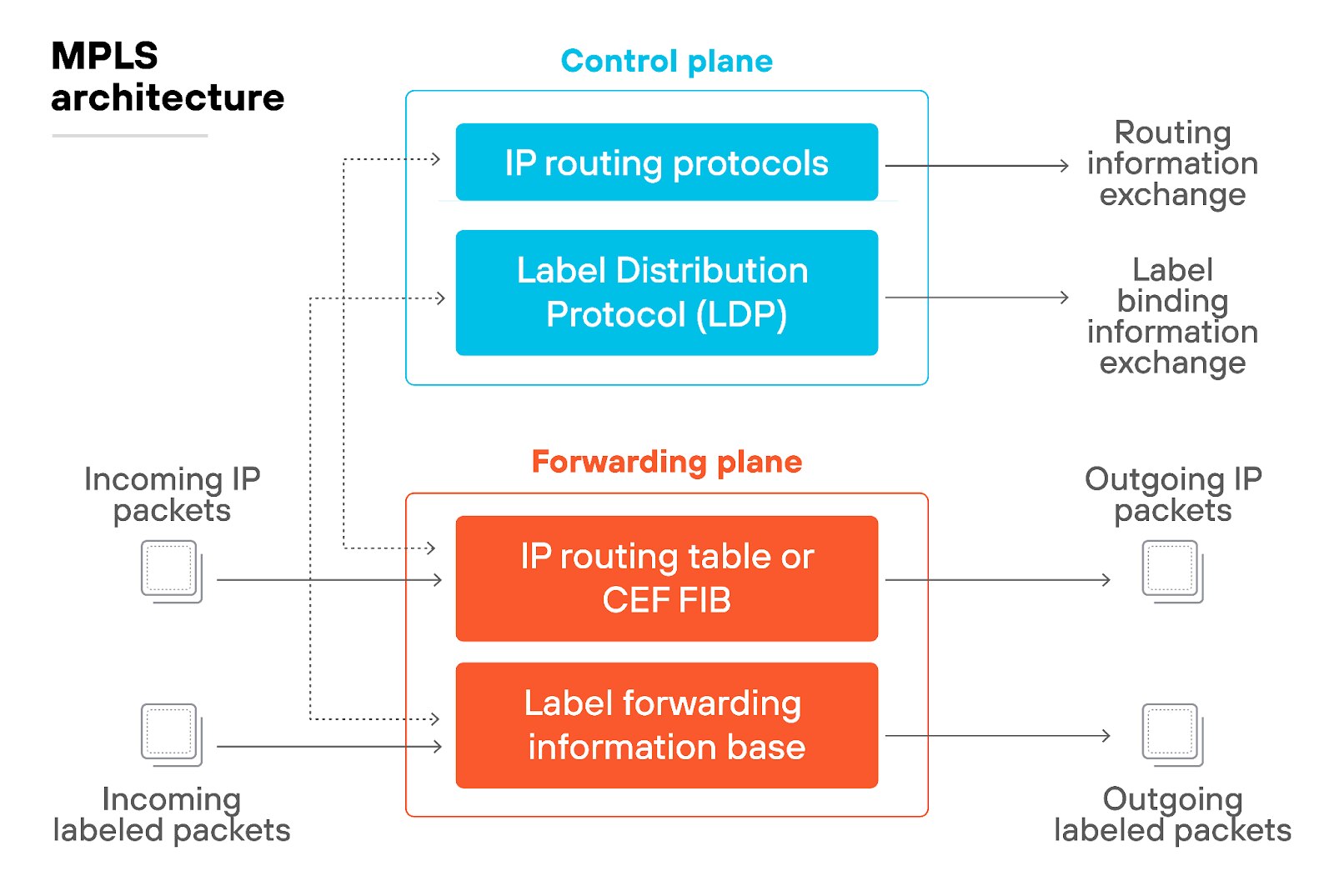
Deploying MPLS could be slow and costly, especially when scaling to multiple locations. Its rigid structure made it challenging to adapt to the changing needs of modern businesses, which increasingly relied on cloud services.
Enter SD-WAN.
SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) emerged around 2014 to address these limitations.
It uses software-defined networking (SDN) principles to abstract the network control layer from the underlying hardware. Which allows SD-WAN to use any available connection type, including broadband, LTE, MPLS, or the public internet.
This optimizes traffic based on current network conditions and application requirements.
SD-WAN brought many improvements. At the same time, there were still enterprises with significant investments in MPLS infrastructure, or the need for the reliability of MPLS for certain critical applications.
This gave rise to hybrid SD-WAN, which combines both MPLS and SD-WAN.
Note: Hybrid SD-WAN is distinct from hybrid WAN. Hybrid SD-WAN specifically integrates traditional MPLS circuits with other WAN connections for dynamic traffic optimization. Hybrid WAN simply uses multiple WAN connections without advanced SD-WAN capabilities.
Further reading:
How does hybrid SD-WAN work?
Hybrid SD-WAN combines the distinct capabilities of multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) and SD-WAN technologies to create a versatile, efficient network architecture.
SD-WAN serves as an overlay that enhances network flexibility and control. It uses software to manage various virtual network layers over existing physical networks. Which allows organizations to direct and reroute network traffic dynamically based on the specific needs of different applications.
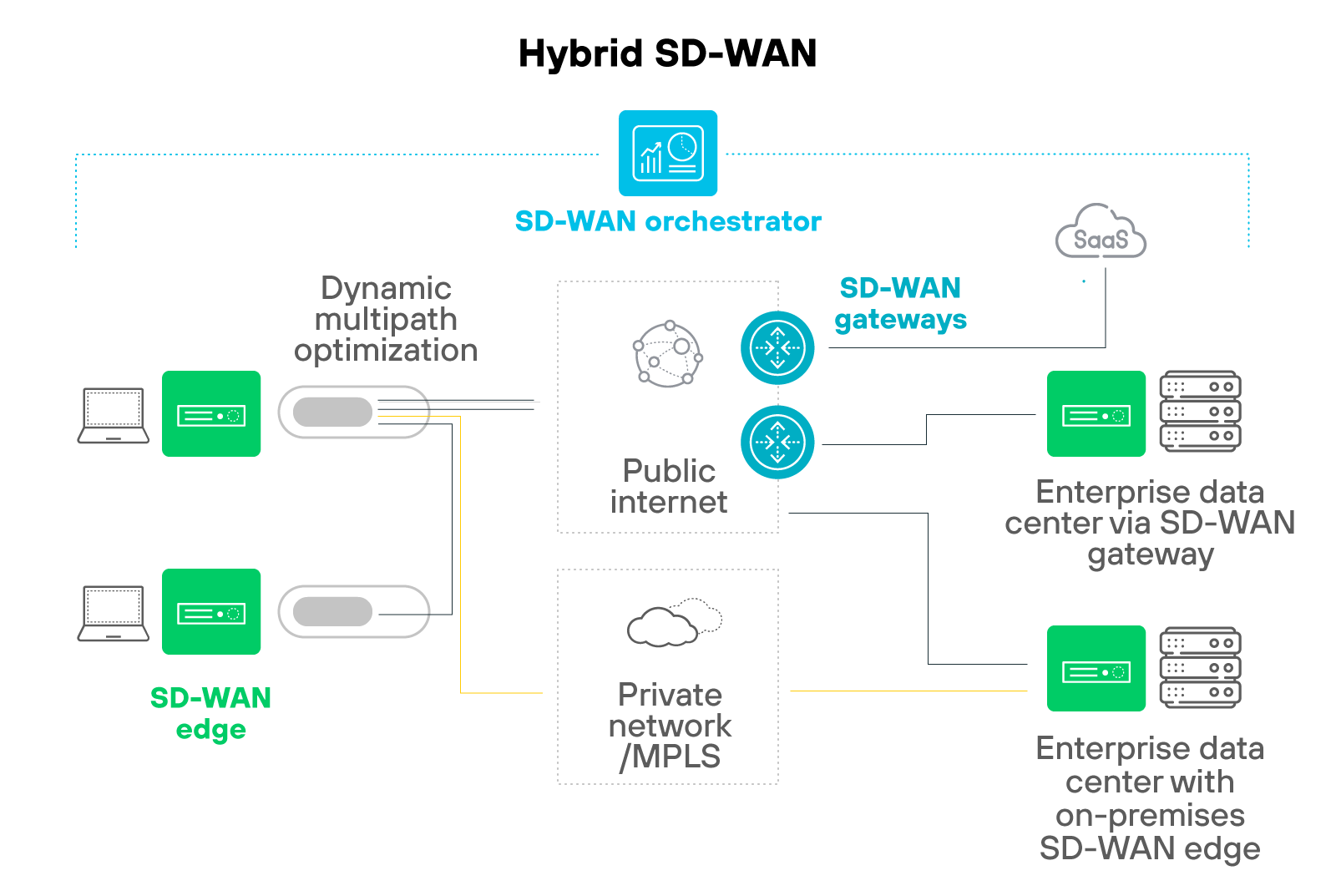
MPLS functions as the underlay, providing the robust, reliable connectivity essential for supporting sensitive or high-priority data transfers. By maintaining MPLS within the hybrid setup, organizations can ensure stable, high-performance connections where necessary—such as for bandwidth-intensive or latency-sensitive applications.
The combination allows the physical infrastructure to support crucial business operations with reliability.
What are the core components of hybrid SD-WAN?
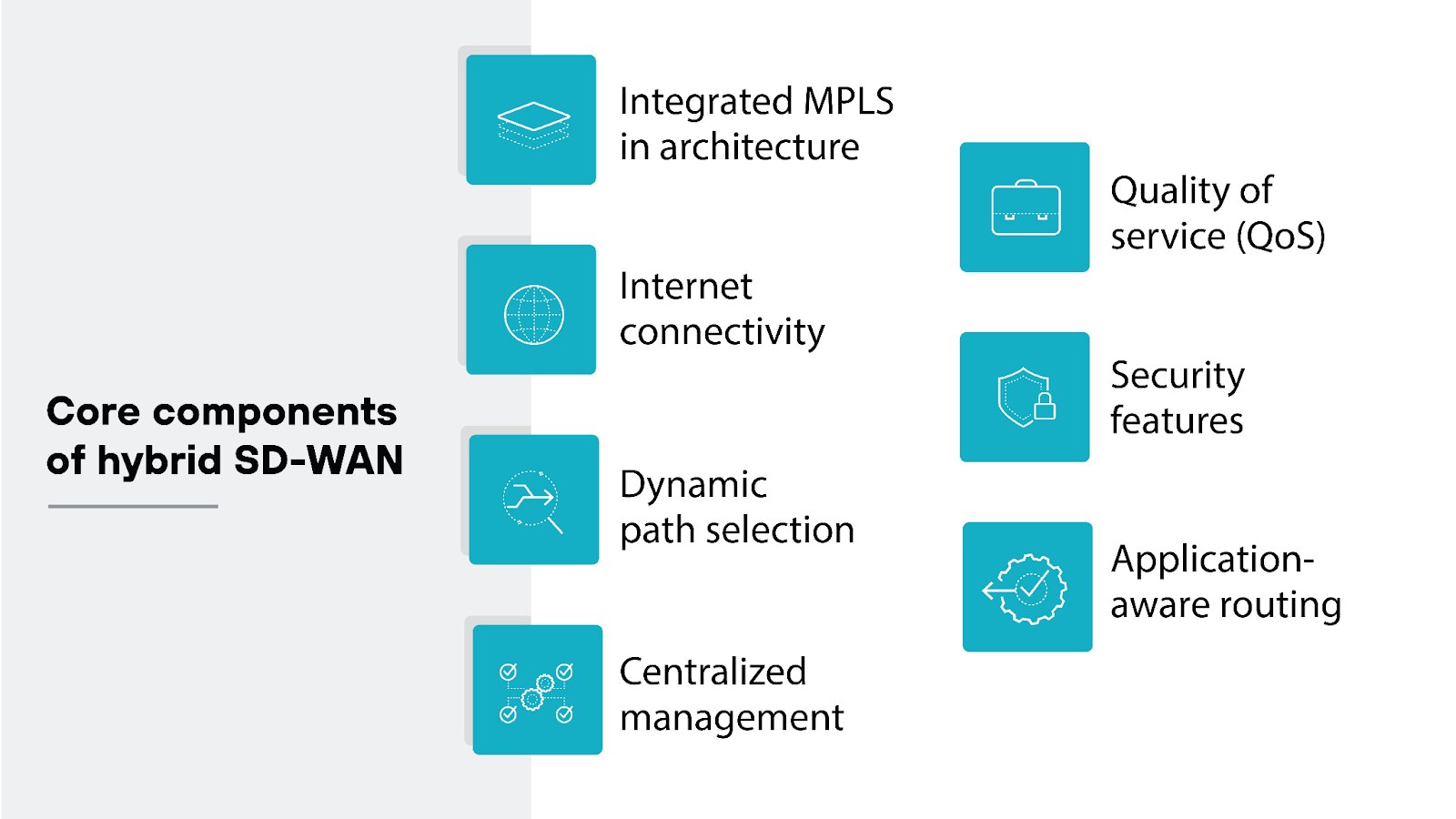
Hybrid SD-WAN infrastructure is fundamentally similar to traditional SD-WAN, incorporating all of the same core components, including:
- Internet connectivity
- Dynamic path selection
- Centralized management
- Quality of service (QoS)
- Security features
- Application-aware routing
Hybrid SD-WAN is unique in that it integrates MPLS into its architecture. The integration results in a network solution that combines the high reliability and low latency of MPLS with the cost-effectiveness and agility of internet-based SD-WAN connections.
What are the benefits of hybrid SD-WAN?
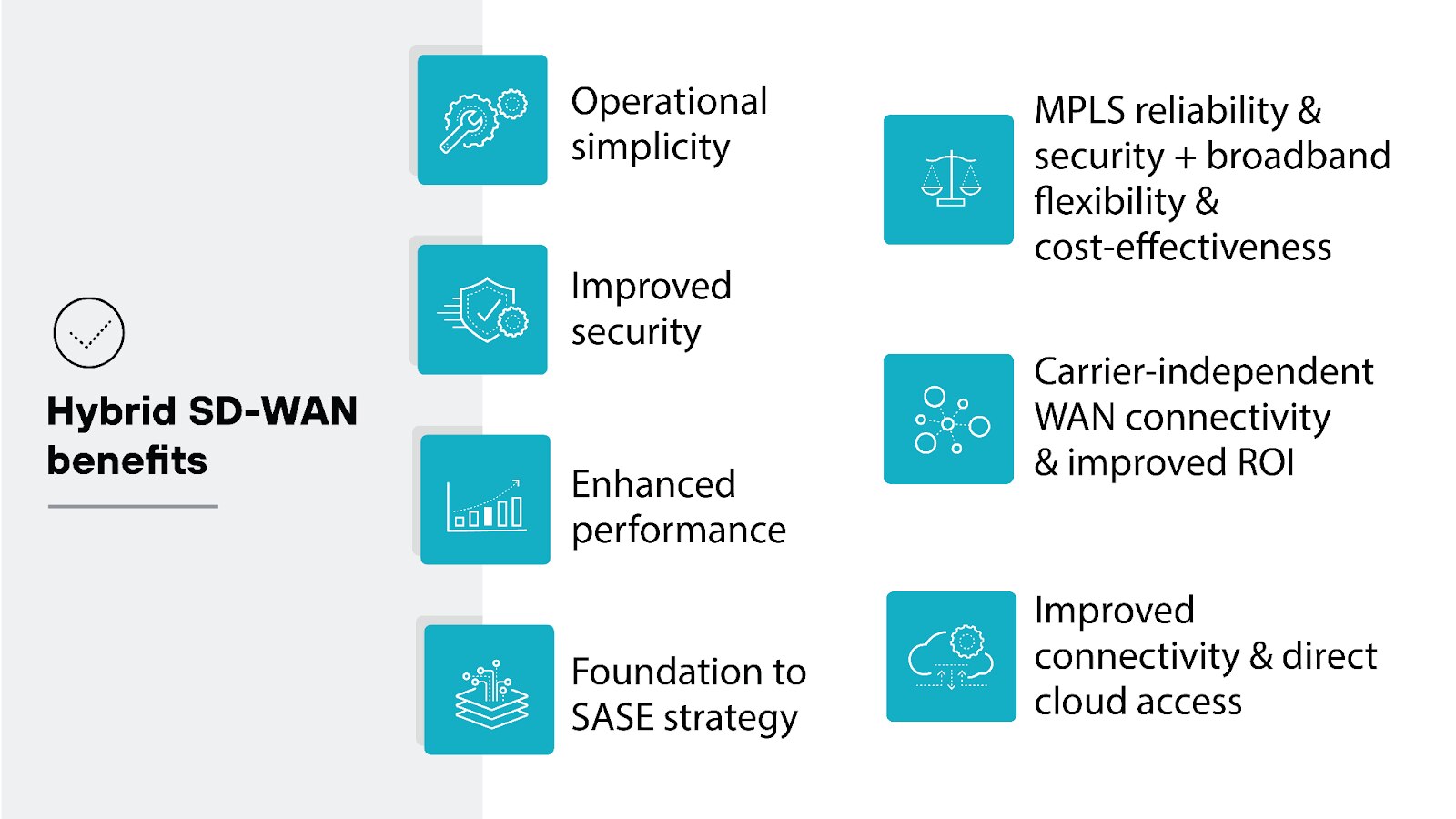
The benefits of hybrid SD-WAN are largely the same as the benefits of SD-WAN, including:
- Operational simplicity
- Carrier-independent WAN connectivity and improved ROI
- Improved security
- Enhanced performance
- Improved connectivity and direct cloud access
- Foundation to SASE strategy
The main distinctive benefit of hybrid SD-WAN is its ability to combine the reliability and security of MPLS with the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of broadband internet.
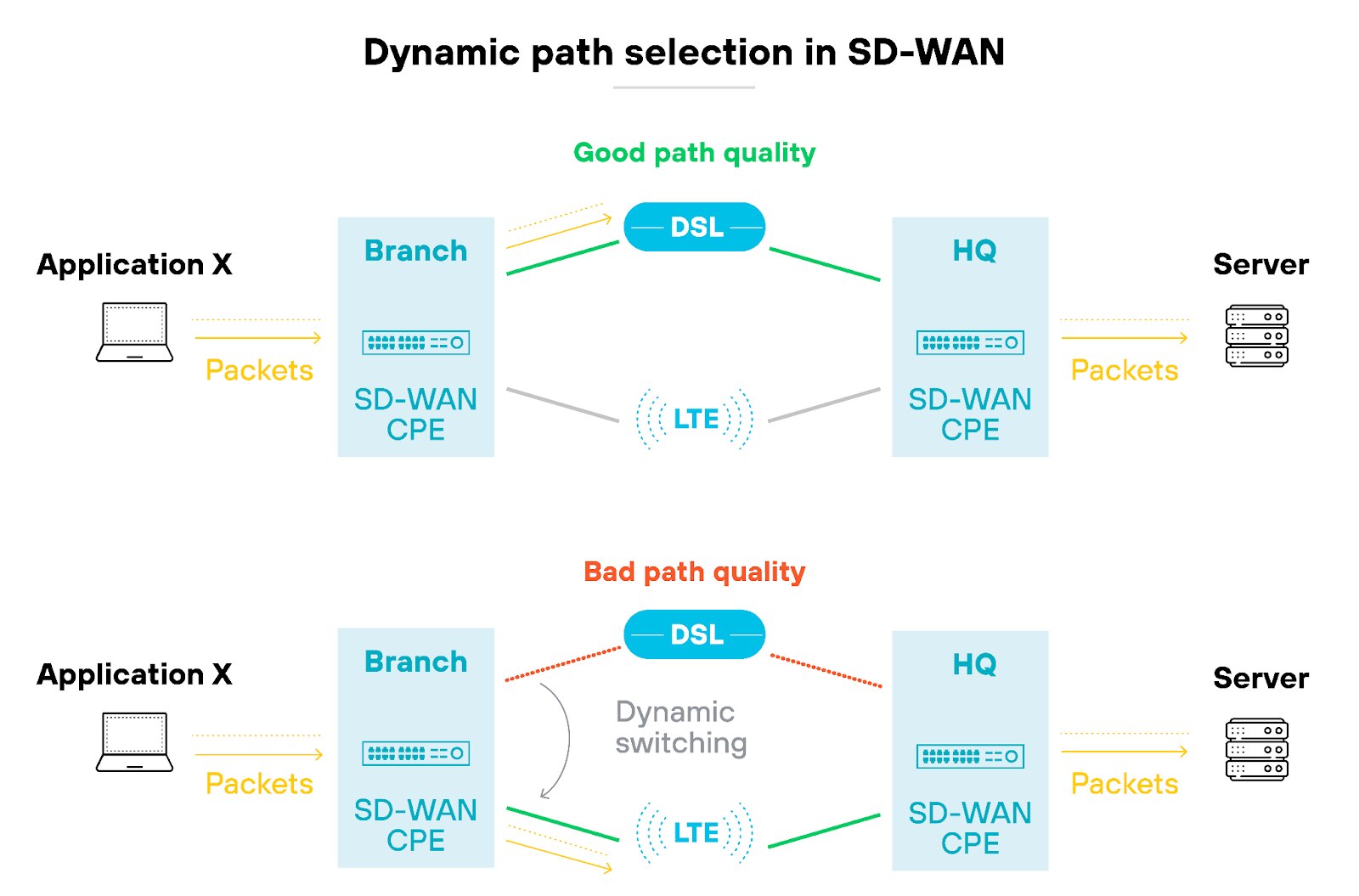
The end result is optimal performance for both critical and non-critical applications. Which is achieved by dynamically routing traffic based on application requirements, like traditional SD-WAN.
Like this:
Further reading: SD-WAN vs. SASE: What’s the Difference?
Use cases for hybrid SD-WAN
Hybrid SD-WAN can be considered a niche solution.
It specifically addresses the needs of organizations that require the reliability and performance of MPLS for mission critical applications while also seeking the flexibility and cost savings of SD-WAN for other types of traffic. This makes it particularly suitable for businesses with complex, multi-site networks that cannot fully transition away from MPLS because of specific operational requirements.
Organizations might choose a hybrid SD-WAN solution when they need a controlled, phased transition from traditional MPLS connections to a more flexible, internet-based network architecture without completely discarding the MPLS infrastructure.
This approach could also work well for businesses with critical real-time applications that demand the reliability and low latency of MPLS. At the same time, it allows them to capitalize on the cost efficiency and agility of SD-WAN for other less critical traffic.
Essentially, hybrid SD-WAN provides a balance that maintains essential performance levels for key applications while transitioning other network traffic to more cost-effective routes.